Machine Learning Use Cases in Master Data Management
Picture this: You’re staring at your screen on a Tuesday morning, watching yet another data quality report that shows 30% duplicate customer records across your systems. Your team spent three weeks manually cleaning product catalogs, only to find new inconsistencies the following month. Sound familiar?
If you’ve been in data management long enough, you’ve probably had this exact experience more times than you’d care to admit. The truth is, traditional master data management approaches while foundational are struggling to keep pace with the sheer volume and complexity of modern enterprise data. But here’s where things get interesting: machine learning is quietly revolutionizing how we think about MDM.
I’ve been working with organizations implementing AI-powered master data management solutions, and the transformation I’ve witnessed is remarkable. Let me walk you through the most impactful use cases that are changing the game for data teams everywhere.
Table of Contents
The Shift from Reactive to Proactive Data Management
Before we dive into specific applications, it’s worth acknowledging something we all know but rarely say out loud: traditional MDM has been largely reactive. We set up rules, wait for problems to surface, then scramble to fix them. It’s exhausting, and frankly, it’s not sustainable.
Machine learning MDM flips this approach entirely. Instead of waiting for data quality issues to emerge, ML algorithms continuously monitor, learn, and adapt to your data patterns. They predict problems before they cascade through your systems and automate corrections that previously required manual intervention.
This shift represents more than just operational efficiency it’s a fundamental change in how we approach data governance and stewardship.
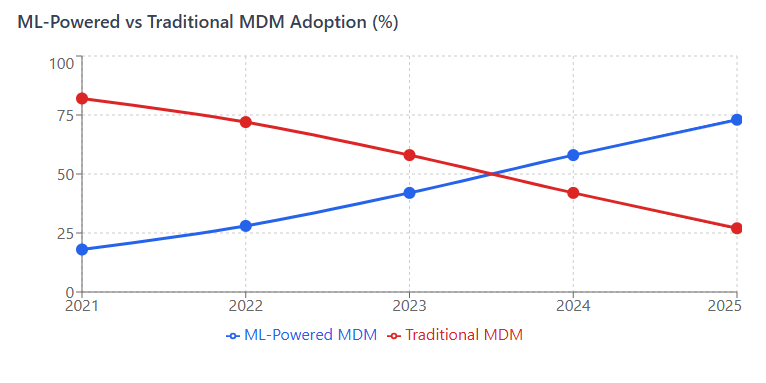
| Traditional MDM | ML-Powered MDM | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Manual rules | Auto learning | 80% faster |
| Reactive fixes | Proactive alerts | Early detection |
| Static patterns | Dynamic adapt | Self-improving |
| Human intensive | AI assisted | Reduced effort |
| Batch processing | Real-time | Instant response |
| High errors | Smart validation | Better accuracy |
Intelligent Data Quality Enhancement
Let’s start with the area where most organizations see immediate impact: data quality. Traditional data management relies heavily on predefined business rules and manual validation processes. But what happens when your customer enters “NYC” instead of “New York City”? Or when product descriptions vary slightly between different source systems?
Automated Data Cleansing That Actually Works
Machine learning algorithms excel at pattern recognition in ways that simple business rules can’t match. Natural language processing models can standardize address formats, company names, and product descriptions by understanding context rather than just applying rigid matching criteria.
I recently worked with a retail client whose product catalog contained over 200 variations of “iPhone” across different suppliers. Traditional cleansing rules would have required extensive manual mapping. Instead, their ML-powered system learned to recognize these variations automatically, standardizing product names while preserving meaningful distinctions like model numbers and storage capacities.
Real-Time Data Validation
Here’s where things get really interesting. Advanced MDM systems now use unsupervised learning to establish baseline patterns for your data, then flag anomalies as they occur. This isn’t just about catching obvious errors it’s about identifying subtle inconsistencies that might indicate upstream process changes or data quality degradation.
The beauty of this approach? The system gets smarter over time, learning from your team’s corrections and validation decisions to improve future predictions.
Revolutionary Entity Resolution and Matching
If data quality is the foundation of MDM, then entity resolution is the architecture. This is where machine learning truly shines, moving us beyond the limitations of deterministic matching rules.
Beyond Simple Fuzzy Matching
Traditional fuzzy matching algorithms work well for obvious similarities, but they struggle with complex scenarios. What if the same customer appears in your CRM as “John Smith,” in your billing system as “J. Smith,” and in your support platform as “Johnny Smith”? Simple similarity scoring often falls short.
Machine learning models approach this differently. They consider multiple data points simultaneously names, addresses, email patterns, transaction histories to build probabilistic confidence scores. These models can identify matches that human reviewers might miss while avoiding false positives that plague rule-based systems.
Cross-System Entity Resolution
One of my favorite implementations involved a financial services company struggling with customer data spread across dozens of systems. Their traditional MDM approach required extensive manual review for potential matches above certain confidence thresholds.
After implementing ML-driven entity resolution, they reduced manual review workload by 70% while actually improving match accuracy. The system learned to recognize subtle patterns in customer behavior and preferences that provided additional matching signals beyond basic demographic data.
Automated Data Classification and Categorization
This is an area where I see tremendous potential that many organizations haven’t fully explored yet. Machine learning can automatically classify and categorize master data based on content, context, and usage patterns.
Think about product hierarchies in retail or manufacturing environments. Instead of manually maintaining category structures, ML algorithms can analyze product descriptions, specifications, and customer behavior to suggest optimal categorization schemes. They can even identify when existing categories no longer reflect actual product relationships.
For customer data, unsupervised clustering algorithms can reveal natural customer segments based on behavior, preferences, and characteristics that might not be apparent through traditional demographic analysis. This automated segmentation becomes invaluable for personalization and targeted marketing initiatives.
Predictive Data Governance
Now we’re getting to the really exciting stuff using machine learning not just to manage current data quality, but to predict and prevent future issues.
Anticipating Data Quality Degradation
ML models can analyze historical data quality trends and system usage patterns to predict when specific data domains are likely to experience quality issues. Maybe customer address data degrades faster during certain seasonal periods, or product information becomes inconsistent following supplier onboarding processes.
This predictive capability allows data stewards to proactively address potential issues rather than constantly playing catch-up.
Automated Policy Enforcement
Similarly to what I’ve discussed regarding <machine learning in spend classification> policy enforcement becomes more nuanced and effective when powered by AI. Instead of rigid rules that often catch legitimate exceptions, ML models learn to understand the intent behind governance policies and apply them contextually.
This approach has proven especially valuable in regulatory environments where data classification and handling requirements are complex but critical for compliance.
Real-World Success Stories
Let me share a few examples that illustrate the practical impact of these capabilities:
A manufacturing company implemented ML-powered product information management to unify data from multiple ERP systems and supplier feeds. Within six months, they reduced product data inconsistencies by 85% while cutting manual data stewardship effort in half. The system learned to recognize equivalent products across different naming conventions and automatically resolved conflicts based on data source reliability and freshness.
Another client in financial services used AI MDM for regulatory compliance, automatically classifying customer data according to privacy regulations across multiple jurisdictions. The ML models learned to identify personally identifiable information in unstructured data fields and apply appropriate handling policies based on customer location and consent status.
These implementations share a common theme: they didn’t replace human expertise but rather amplified it, allowing data professionals to focus on strategic initiatives instead of routine maintenance tasks.
Practical Implementation Considerations
If you’re considering ML-powered MDM, here are some lessons learned from successful implementations:
Start with a clear understanding of your current data quality baseline. Machine learning algorithms need good training data, and you’ll want to measure improvement from a known starting point. Don’t try to solve everything at once begin with your most critical data domains where quality issues have the highest business impact.
Integration with existing systems requires careful planning. Most organizations aren’t ready to replace their entire MDM infrastructure overnight. Look for solutions that can augment your current tools rather than requiring complete replacement.
Change management is crucial. Your data stewardship team will need to adapt to new workflows and learn to work effectively with AI-powered recommendations. Invest in training and establish clear processes for human oversight and intervention.
Similar to the considerations I’ve outlined for <Machine Learning RFP> processes, vendor evaluation should focus on explainability and transparency. You need to understand why the system makes specific recommendations, especially in regulated environments.
Looking Forward
The intersection of artificial intelligence and master data management represents one of the most significant advances in enterprise data management since the introduction of data warehousing. We’re moving from reactive, rule-based systems to proactive, intelligent platforms that learn and adapt.
But perhaps most importantly, AI MDM isn’t about replacing human judgment it’s about enhancing it. The most successful implementations I’ve seen combine machine learning capabilities with human expertise and domain knowledge to create data management programs that are both highly automated and deeply contextual.
The organizations that embrace this evolution now will have a significant advantage in data quality, operational efficiency, and decision-making capabilities. The technology is mature enough for production use, and the business case is compelling for most enterprise environments.
Your data doesn’t have to be a constant source of frustration and manual effort. With the right approach to machine learning in master data management, it can become one of your organization’s most valuable and well-managed assets.
The question isn’t whether AI will transform MDM it’s whether your organization will be leading that transformation or catching up to it.
What is machine learning MDM?
AI-powered master data management that uses algorithms to automate data quality, matching, and governance tasks.
How does ML improve data matching?
It analyzes multiple data points simultaneously to identify matches that rule-based systems miss while reducing false positives.
Can ML MDM integrate with existing systems?
Yes, most ML MDM solutions can augment current tools rather than requiring complete infrastructure replacement.
What’s the typical ROI timeline for AI MDM?
Most organizations see measurable improvements in data quality and reduced manual effort within 3-6 months of implementation.
Do I need a data science team to implement ML MDM?
No, modern ML MDM platforms are designed for business users with built-in algorithms and user-friendly interfaces.